| Product Advantage
1)Increased Capacity: By combining 16 batteries into a single pack, the overall capacity of the battery pack is significantly increased. This means that the pack can store more energy and provide power for a longer duration compared to individual batteries or smaller packs. It is especially beneficial for devices with high energy demands or in situations where extended runtime is required.
2)Higher Voltage Output: By connecting multiple batteries in series, a 16-pack battery pack can provide a higher voltage output than a single battery. This can be advantageous for devices that require a specific voltage level to operate efficiently or that are designed to work with higher voltage inputs.
3)Enhanced Power Output: In some cases, a 16-pack battery pack may be configured to provide higher power output compared to individual batteries or smaller packs. This can be useful for devices that require a high current or power level to operate, such as power tools or electric vehicles.
4)Improved Reliability: With a 16-pack battery pack, there is redundancy in the system. If one or a few batteries fail or lose capacity over time, the remaining batteries can continue to provide power. This redundancy helps to maintain the overall reliability of the battery pack, ensuring continuous operation even if some batteries degrade or fail.
5)Flexibility and Scalability: A 16-pack battery pack offers flexibility and scalability in terms of energy storage. It can be used in various applications, ranging from small electronic devices to larger systems. Additionally, if additional power or capacity is needed, multiple 16-pack battery packs can be connected in parallel or series to achieve the desired energy requirements.
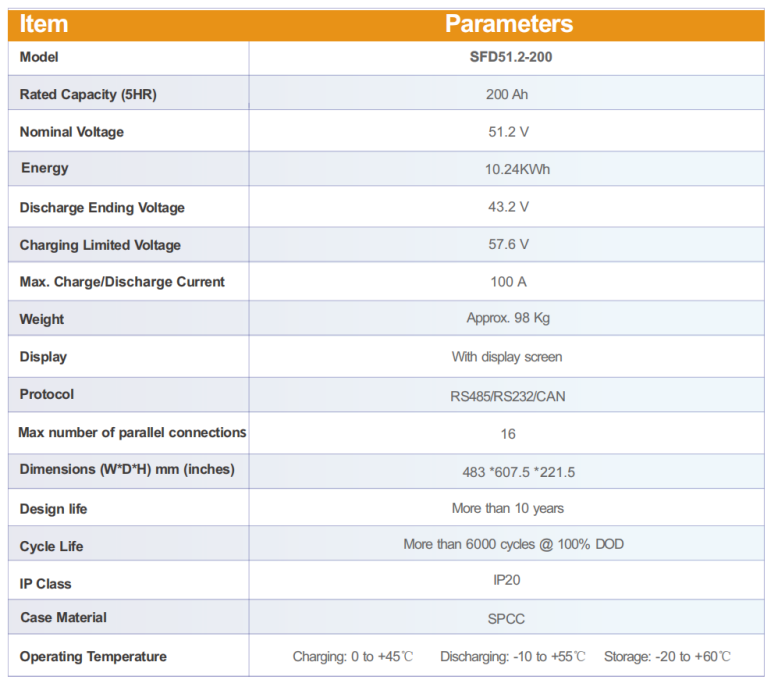
| Technical Parameters
| Product Uses
1)High Power Demands: When a device or system requires a substantial amount of power, using 16 battery packs can provide the necessary power output. This is particularly relevant in applications such as high-performance electric vehicles, large-scale robotics, or industrial equipment that demand significant power to function optimally.
2)Enhanced Redundancy: By using 16 battery packs, redundancy is increased, enhancing the reliability and availability of power. If one or more battery packs fail or experience issues, the remaining packs can continue to provide power, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous operation.
3)Extended Runtime: Combining 16 battery packs can significantly increase the overall capacity and runtime compared to a single battery pack. This is beneficial in situations where prolonged operation or extended periods without access to charging is required, such as outdoor events, off-grid locations, or emergency backup power.
4)Scalability and Flexibility: Utilizing 16 battery packs allows for scalability and adaptability to varying power requirements. Depending on the specific needs, the number of battery packs can be adjusted to match the desired power output or capacity. This scalability is advantageous in applications where power demands may change or where future expansion is anticipated.
5)Load Balancing: When using multiple battery packs, load balancing techniques can be employed to distribute the power demand evenly across the packs. This ensures that each pack is utilized efficiently and prevents overloading or uneven discharge, which can help extend the overall lifespan of the battery packs.
| FAQ
1)What is a 16-group battery pack?
A 16-group battery pack refers to a configuration where 16 individual battery packs are connected together to form a larger battery system. Each group typically consists of multiple batteries connected in series or parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity.
2)What are the advantages of using a 16-group battery pack?
Some advantages of using a 16-group battery pack include:
Higher voltage and capacity: By combining 16 battery packs, the overall voltage and capacity of the battery system are increased, allowing for higher power output and longer runtime.
Enhanced redundancy: If one or more battery packs fail, the remaining packs can continue to provide power, improving the reliability and availability of the battery system.
Load balancing: With multiple battery packs, load balancing techniques can be employed to distribute the power demand evenly across the packs, optimizing their performance and lifespan.
Scalability: The use of multiple battery packs allows for scalability, as additional packs can be added or removed to meet changing power requirements.
Flexibility: A 16-group battery pack provides flexibility in terms of power distribution, making it suitable for applications where power needs to be delivered to multiple devices or systems.




















